Our Pipeline.
The asialoglycoprotein receptor (ASGPR) is an endocytotic cell surface receptor that plays a key role in a natural process through which endogenous proteins are internalized and degraded in the hepatocyte endolysosome. ATACs (ASGPR Targeting Chimeras) are designed to harness this natural ASGPR degradation pathway. They are heterobifunctional molecules comprised of a ligand that binds to ASGPR, connected via a chemical linker to a second ligand that binds to a target disease-causing extracellular protein. ATACs work by binding to and shuttling targeted proteins from the circulation to the hepatocyte endolysosome, where the unwanted proteins are degraded.
We are advancing multiple ATAC extracellular protein degrader programs across several therapeutic areas with high unmet need. Avilar’s target protein ligands span several modalities including biologic, peptide, and small molecule.
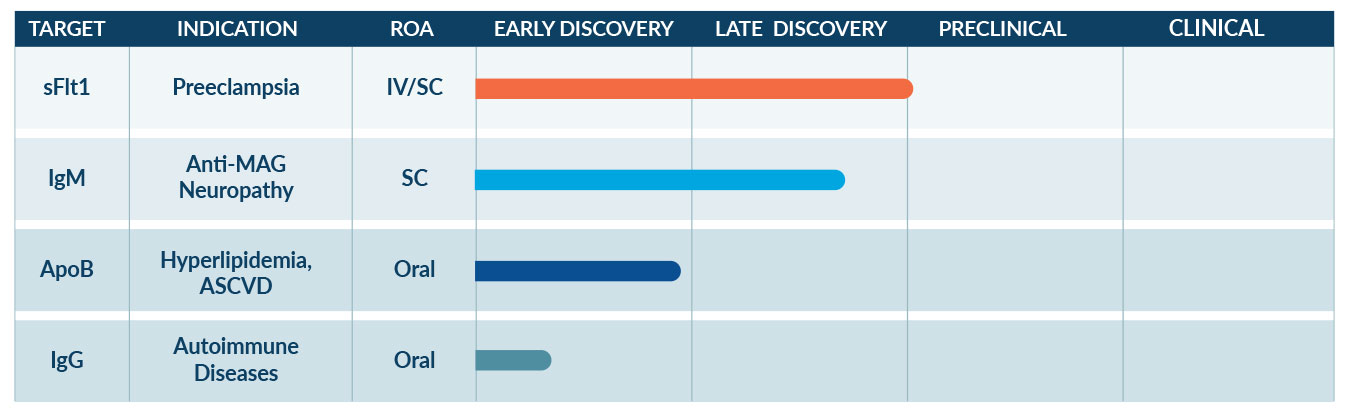
sFlt1 ATAC Program for Preeclampsia
Preeclampsia is a potentially life-threatening disease of pregnancy, affecting 2-8% of pregnancies globally, with complications for both mothers and babies. Despite decades of research, there is no effective treatment except to deliver the baby.
Avilar’s solution for preeclampsia is to use an ATAC to selectively bind and remove from circulation a protein called sFlt1, which has been identified as a central driver of preeclampsia. As a result of lowering sFlt1, disease progression can be stopped, and potentially reversed, allowing the pregnancy to be prolonged until the baby can be safely delivered and start life with fewer complications. Importantly, the ATAC is designed not to enter the baby’s circulation, and the dosing can be personalized to provide optimal benefit for mother and baby. Learn more about Avilar’s work in preeclampsia.
IgM ATAC Program for Anti-MAG Neuropathy
Anti-MAG Neuropathy (or AMN) is a chronic, progressive neurological disease affecting the peripheral nerves in the arms, legs, hands and feet. It impacts an estimated 7,000 patients in the US. AMN causes gradual numbness, tingling, and weakness that typically start in the hands and feet and gradually spread towards the core. Eventually it can progress to severe disability requiring a walker or even a wheelchair. It can also be very painful and lead to tremor in the hands that prevents patients from caring for themselves. There are no approved therapies for AMN.
AMN is caused by a specific type of circulating autoantibody called anti-MAG IgM that attacks the protective sheath which surrounds and insulates the nerve fibers. Avilar scientists have created an ATAC molecule which selectively binds to IgM and removes it from circulation. As a result of removing the disease-causing autoantibodies we expect to heal the underlying pathology of the disease, improve symptoms and give back to patients the mobility and quality of life they have lost.
Oral ApoB ATAC Program for Cardiovascular Disease
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) affects around 26 million people in the US and stands as a leading cause of both disability and death across the developed world.
Elevated plasma levels of several different types of cholesterol-containing particles, known as lipoproteins, have been identified as key risk factors for heart attack and stroke. The best known of these is LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein), however, other lipoproteins such as Lipoprotein(a) (Lp(a)) and Triglyceride-Rich Lipoproteins (TRLs) are increasingly recognized as important contributors to cardiovascular risk, in particular in highly prevalent diseases such as diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Notably, Lp(a) and TRLs are poorly addressed by currently approved therapies. We are developing an oral ATAC that uses a small molecule that binds to ApoB, a protein found on the surface of all these lipoproteins. By simultaneously reducing several types of key atherogenic lipoproteins, Avilar’s ApoB ATAC aims to be the most effective treatment to reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke, both in patients with and without preexisting cardiovascular disease.
Oral IgG ATAC Program for Autoimmune Disease
Many autoimmune diseases are driven primarily by IgG autoantibodies that attack otherwise healthy normal tissues. Lowering IgG is a proven way to improve symptoms of these diseases but all the current approaches involve injectable drugs or invasive techniques.
Avilar scientists are working towards the first oral pill, an ATAC that can be taken once daily to lower IgG providing a more convenient and accessible treatment for autoimmune diseases driven by IgG autoantibodies.
References
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/pre-eclampsia
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0165572821002526?via%3Dihub

